South Koreans may soon be able to carry a device inside their own bodies in the form of a bespoke tattoo that automatically alerts them to potential health problems, if a science team's project bears fruit.
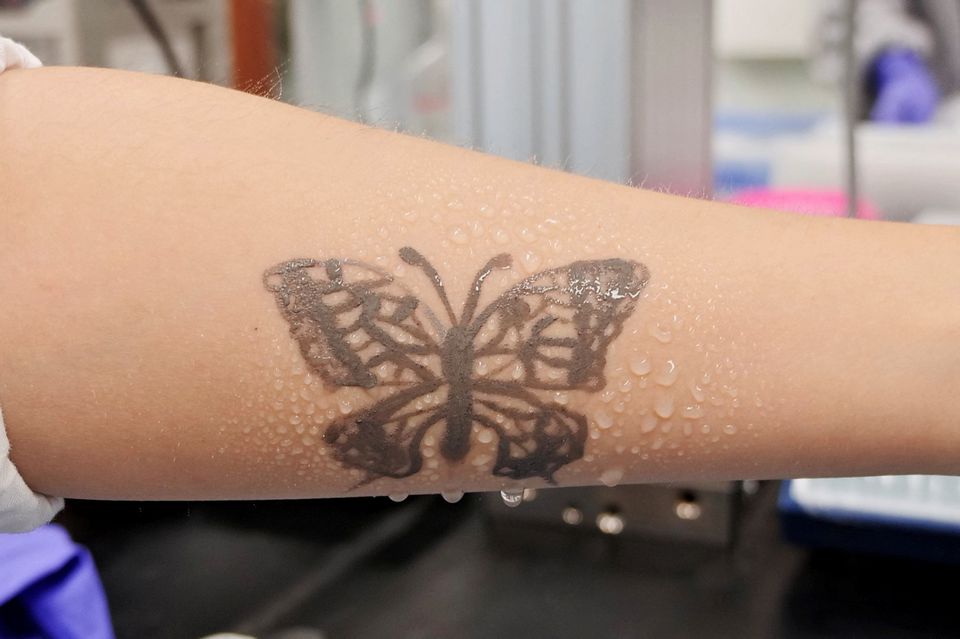
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in the city of Daejeon southwest of Seoul have developed an electronic tattoo ink made of liquid metal and carbon nanotubes that functions as a bioelectrode.
Hooked up to an electrocardiogram (ECG) device or other biosensor, it can send a readout of a patient's heart rate and other vital signs such glucose and lactate to a monitor.
|
|
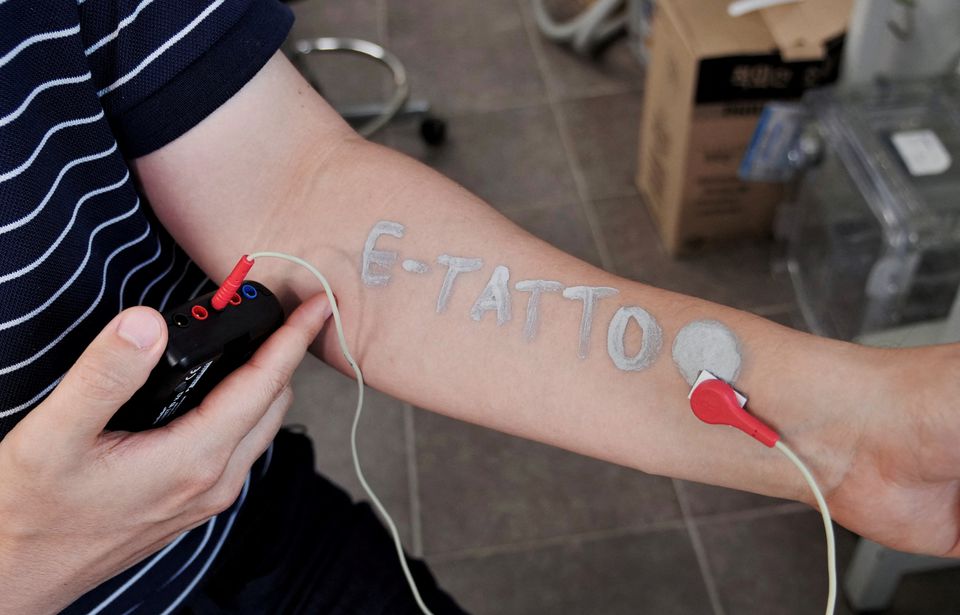
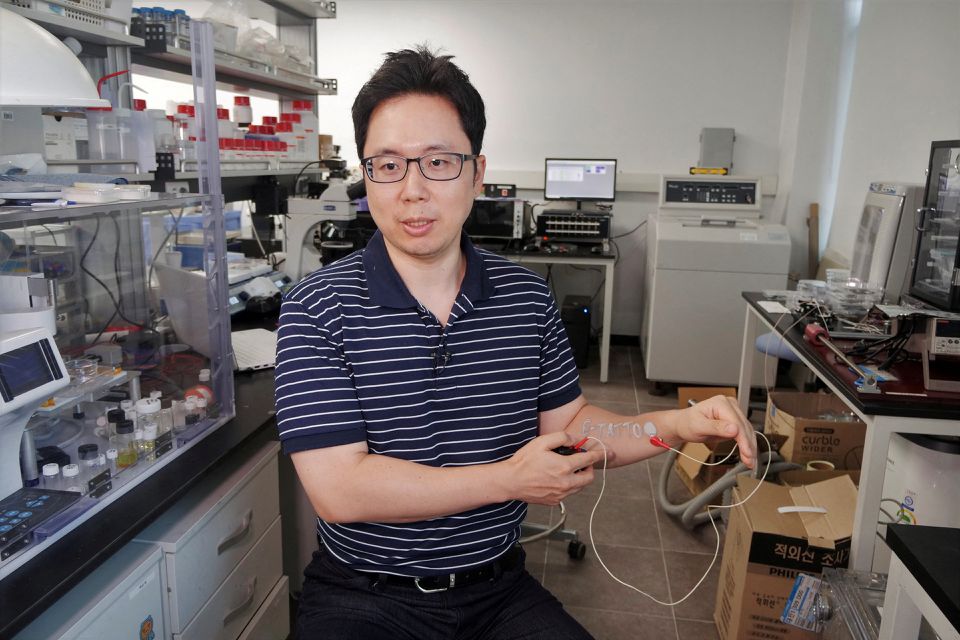
| Steve Park, Materials Science & Engineering professor at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), demonstrates an electronic tattoo (e-tattoo) on his arm connected with an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring system in Daejeon, South Korea, July 26, 2022. Photo: Reuters |
The researchers eventually aim to be able to dispense with biosensors.
"In the future, what we hope to do is connect a wireless chip integrated with this ink, so that we can communicate, or we can send signal back and forth between our body to an external device," said project leader Steve Park, a materials science and engineering professor.
Such monitors could in theory be located anywhere, including in patients' homes.
The ink is non-invasive and made from particles based on gallium, a soft, silvery metal also used in semiconductors or in thermometers. Platinum-decorated carbon nanotubes help conduct electricity while providing durability.
"When it is applied to the skin, even with rubbing the tattoo doesn't come off, which is not possible with just liquid metal," Park said.
|
|
| Steve Park, Materials Science & Engineering professor at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), demonstrates an electronic tattoo (e-tattoo) on his arm connected with an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring system in Daejeon, South Korea, July 26, 2022. Photo: Reuters |